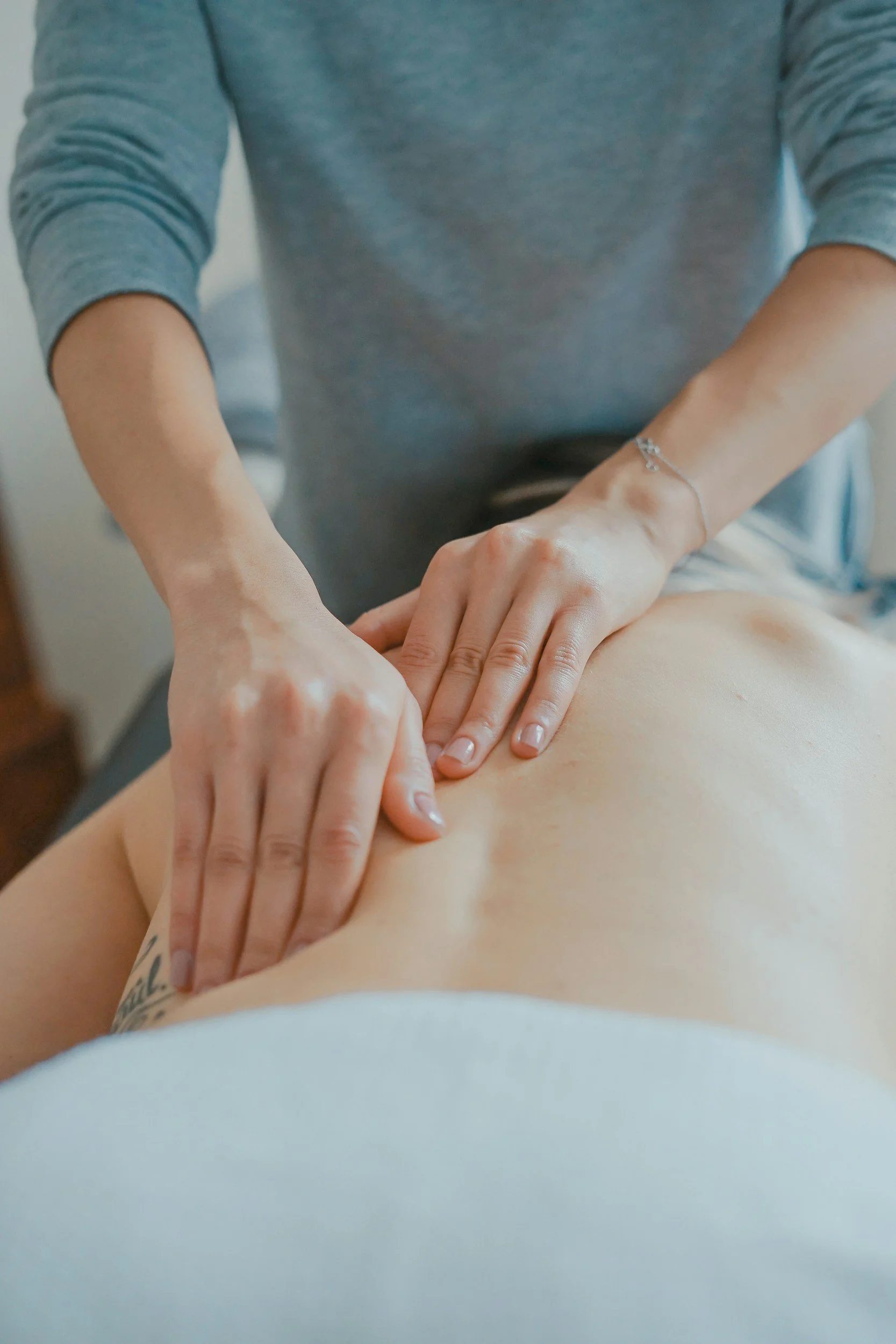
One of the biggest concerns for anyone entering the massage therapy field is how to secure a job immediately after graduation. The massage industry is competitive, and employers often seek candidates who not only hold the necessary licenses but also have hands-on experience. This “experience factor” can make or break your chances of getting hired quickly.
Fortunately, there is a solution that addresses this challenge head-on. By choosing a massage therapy program that emphasizes real client experience during training, you can graduate ready to work and confident in your skills. Here’s why experience matters so much and how it can help you get hired right after graduation.
Why Experience Is Essential for Massage Therapists
Massage therapy is a hands-on profession where practical skills are just as important as theoretical knowledge. While textbooks and lectures provide the foundation, nothing replaces the confidence gained from working with real clients.
Employers want to hire therapists who can demonstrate proficiency in different massage techniques, understand client needs, and maintain professionalism. Having experience means you have already navigated common challenges such as client communication, adapting pressure and techniques, and managing session flow.
Without this experience, new graduates often struggle to convince employers they are ready to handle the demands of the job. This can lead to longer job searches or accepting positions that do not match their career goals.
How Alpha School of Massage Solves the Experience Problem
Alpha School of Massage has designed its Advanced Massage Program with the experience factor in mind. Unlike programs that focus mainly on classroom instruction, Alpha integrates extensive hands-on practice into the curriculum.
Students perform hundreds of massages on paying clients in a supervised setting. This real-world experience allows them to refine their skills, receive feedback, and build a strong professional portfolio before graduation.
This approach ensures Alpha graduates are not just licensed but truly ready to work from day one. When they walk into a job interview, they can confidently share their client work history and demonstrate their abilities.
The Benefits of Gaining Experience During Training
Confidence in Your Skills
Performing numerous massages during training builds confidence. You learn how to adjust techniques for different body types and conditions, handle unexpected situations, and provide excellent client care.
A Strong Resume
Employers appreciate candidates who bring practical experience. Listing hundreds of client sessions and positive evaluations on your resume sets you apart from other new graduates.
Networking Opportunities
Working with real clients often leads to networking and referrals. Building relationships within the community can open doors to job opportunities or private practice clients.
Better Understanding of the Profession
Hands-on experience helps you understand the realities of being a massage therapist, including time management, client expectations, and business aspects. This knowledge prepares you for success beyond the classroom.
Tips for Leveraging Your Experience to Get Hired Quickly
Highlight your client session numbers and types of massage techniques practiced on your resume and during interviews.
Share testimonials or evaluations from clients if available to showcase your professionalism and skill.
Demonstrate your readiness to work by discussing how your training prepared you for real-world scenarios.
Use your network from school and clinical practice to seek job leads or mentorship.
Continue learning and expanding your skills even after graduation to stay competitive.
Why Choose Alpha School of Massage
With more than 30 years of experience, Alpha School of Massage understands what it takes to prepare students for successful careers. Their Advanced Massage Program’s emphasis on client experience ensures graduates leave with the skills and confidence employers demand.
The affordable tuition and debt-free payment plan make it accessible, while the supportive instructors guide students every step of the way.
Getting hired as a massage therapist right after graduation is no longer a problem when you have the right experience. The experience factor is crucial in demonstrating your readiness to employers and setting yourself apart in a competitive job market.
By choosing a program like Alpha School of Massage that prioritizes hands-on client work during training, you graduate not only licensed but truly prepared to succeed. With confidence, a strong resume, and real-world skills, your path to employment becomes clearer and faster.
If you want to solve the hiring challenge and start your massage therapy career on the right foot, consider a program that values experience as much as education. Your future clients and employers will thank you.